Introduction

In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, Solana has emerged as a formidable player, captivating the attention of enthusiasts and investors alike. Launched in March 2020, Solana is a high-performance blockchain platform designed to provide fast and cost-effective decentralized applications (DApps) and crypto projects.
Overview
Speed and Scalability
Solana stands out for its remarkable speed and scalability. It utilizes a unique consensus mechanism known as Proof of History (PoH), which timestamps transactions before they are included in a block. This innovative approach significantly enhances the overall throughput of the network, allowing it to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS). This places Solana ahead of many other blockchain platforms, making it an attractive choice for developers seeking high-performance solutions.
Financial Landscape
From a financial perspective, Solana's native cryptocurrency is SOL. SOL has experienced substantial growth, and its market capitalization has surged, reflecting the growing confidence in the platform. As of the latest data, SOL has not only established itself as a sought-after investment but also serves as the utility token for various functions within the Solana ecosystem.
Technical Details
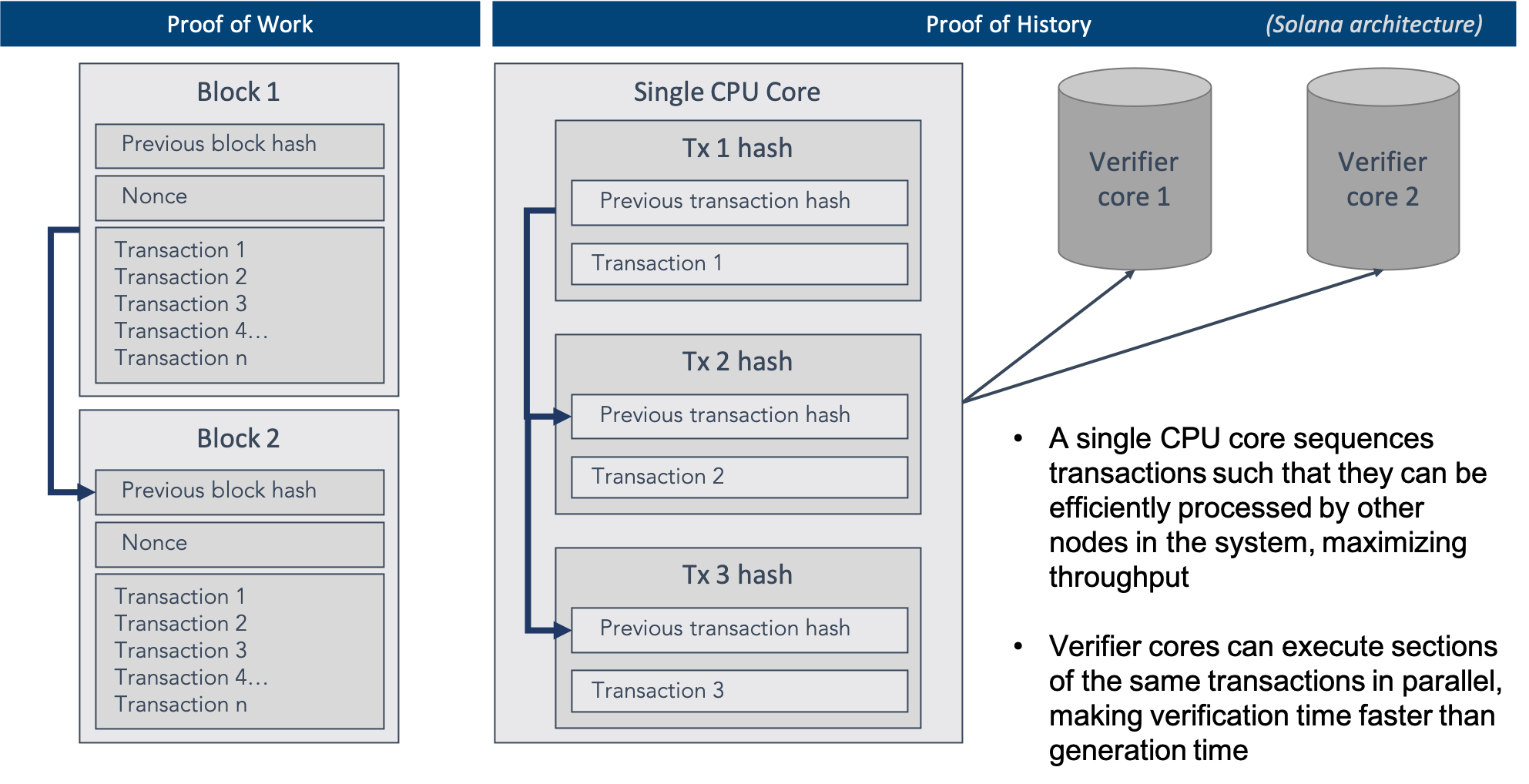
Architecture
1. Proof of History (PoH)
At the core of Solana's architecture is Proof of History (PoH), a groundbreaking consensus algorithm that creates historical records for each transaction before reaching consensus. PoH acts as a verifiable source of time for the network, enhancing overall efficiency and allowing nodes to agree on the order of transactions quickly.
2. Tower BFT Consensus
Solana employs a variant of the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) consensus algorithm called Tower BFT. This consensus mechanism, combined with PoH, contributes to the platform's exceptional scalability and speed. Tower BFT ensures that the network remains secure and resilient against malicious actors.
3. Gulf Stream
Gulf Stream is Solana's optimization for data propagation, reducing the time taken for nodes to synchronize with the network. This feature plays a crucial role in maintaining the high throughput of transactions, further enhancing Solana's overall performance.
Smart Contracts and Tokens

Solana supports smart contracts through its native programming language, Rust. Developers can create decentralized applications and deploy them on the Solana blockchain. Let's explore how to create a simple Solana smart contract and deploy it:
How to Create a Solana Smart Contract
Install Solana Tool Suite:
- Begin by installing the Solana Tool Suite, which includes essential tools like the Solana Command-Line Interface (CLI).
Set Up a Solana Project:
- Create a new Solana project using the
solana initcommand. This initializes the project structure.
- Create a new Solana project using the
Write the Smart Contract:
- Use Rust to write the smart contract. For example, a basic token smart contract that mints tokens can be created.
// my_token.rs
#![cfg(feature = "program")]
use solana_program::{
account_info::{next_account_info, AccountInfo},
entrypoint,
entrypoint::ProgramResult,
msg,
program_error::ProgramError,
pubkey::Pubkey,
system_instruction,
sysvar::{rent::Rent, Sysvar},
};
entrypoint!(process_instruction);
fn process_instruction(
program_id: &Pubkey,
accounts: &[AccountInfo],
_instruction_data: &[u8],
) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Processing instruction");
let accounts_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let account = next_account_info(accounts_iter)?;
// Your logic to mint tokens goes here
Ok(())
}
Build and Deploy:
- Build the smart contract using
cargo build-bpfand deploy it to the Solana blockchain.
- Build the smart contract using
Interact with the Smart Contract:
- Once deployed, you can interact with the smart contract using Solana wallets or other tools.
This simple example illustrates the basic steps to create and deploy a Solana smart contract. Developers can build upon this foundation for more complex DApps and DeFi projects.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving realm of blockchain, Solana has positioned itself as a frontrunner, combining speed, scalability, and a robust technical foundation. Its architecture, featuring innovative elements like Proof of History and Tower BFT, sets it apart in the competitive landscape. As Solana continues to gain traction, it represents a promising avenue for developers and investors looking to engage with a high-performance blockchain platform.

